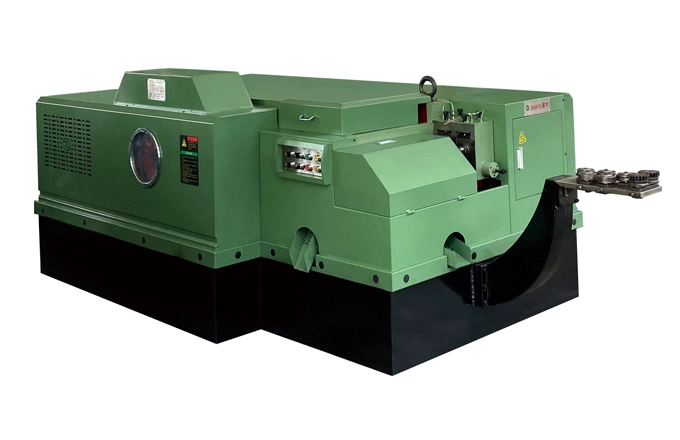
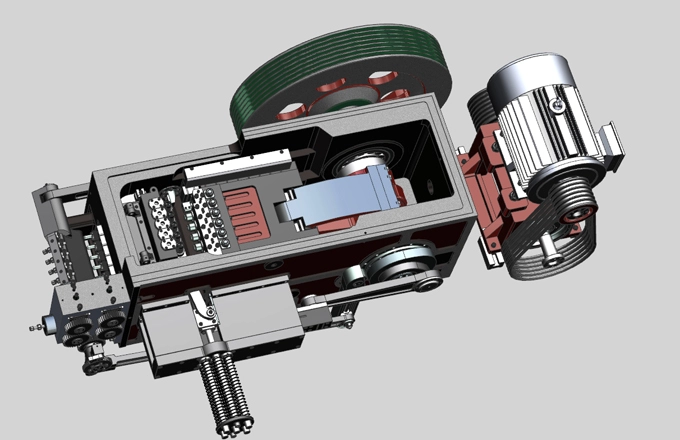
Characteristics of the Multi-Station Cold Forging Machine
The multi-station cold forging machine selects the cold forging method to automatically forge various hexagonal nuts from disc or bar materials, producing standard hexagonal nuts after tapping. The bar material is fed through a roller drive, and processes such as sequential feeding, cutting, ball pressing, angle pressing, and punching are completed in one machine. The cold forging workstations are arranged horizontally, ensuring accurate positioning, stable operation, and convenient maintenance, making it suitable equipment for manufacturers aiming for mass production of nuts.

Key Characteristics of the Multi-Station Cold Forging Machine
Open-close type clamps for workpiece transmission: Each clamp’s opening and closing time can be adjusted individually.
Full-circle sleeve cutter: Ensures a flat cut.
Horizontal arrangement of forging stations: Improves positioning accuracy.
Linkage transmission method: Main action mechanisms (like cutting, pushing the die, feeding) use linkage methods.
Large coil feeding: Meets the feeding requirements for large coils.
Thread rolling mechanism: Enables the automatic production line from cutting, forging to thread rolling for bolts and screws.
Die pushing at the third station: Suitable for edge cutting or forging processes, with easy conversion and adjustment.
Punching mechanism for each station: Each station has a punching mechanism that can be adjusted individually.
Pneumatically controlled clutch and brake: Allows the main motor to start under no load, with precise inching, convenient for machine debugging, and ensures the main slide stops automatically at the rear stop point when the machine stops.
Proper Maintenance and Operation of the Multi-Station Cold Forging Machine
The cold forging machine ensures good surface quality and high dimensional accuracy. Due to the cold work hardening during the forging process, the deformation should not be too large to reduce the chances of cracking. This product boasts high forming efficiency, stable power, and involves a significant one-time capital investment.
Internal cleaning: After prolonged use, grease, carbon deposits, sediments, and rust can accumulate inside the cold forging machine. Regularly clean the interior to ensure the normal position and reaction force of the brake pedal.
Brake system inspection: Disassemble the brake valve and repair or replace it as needed. Check the hydraulic cylinder piston and seals, ensuring there are no damages or leaks in the brake oil pipeline and connectors.
Brake air pressure check: Ensure the brake air pressure ranges between 0.45 to 0.70 Mpa, and regularly check the connections and sealing of the brake system.
Brake system exhaust: Eliminate air from the brake system to ensure effective braking.
Brake maintenance: Regularly inspect and maintain the brake to ensure it functions correctly.
Common Problems and Solutions for the Cold Forging Machine
Due to the continuous production under heavy loads and the high degree of automation, most of the mechanical movements of the cold forging machine are controlled by a crankshaft or cam, causing periodic reciprocating or swinging movements. This can lead to significant forces and impacts, potentially damaging the equipment.
Improvement of the main transmission part: Adjust the forging speed and the number of slider strokes according to cold forging process requirements, ensuring the equipment operates stably under high loads.
Material selection and improvement: Enhance the materials of the machine’s mechanisms and key parts to reduce damage caused by material imperfections.
Regular maintenance and inspection: Conduct regular maintenance and inspection of the cold forging machine to promptly identify and resolve potential issues, thereby extending the equipment's service life.

(1).webp)

 English
English